

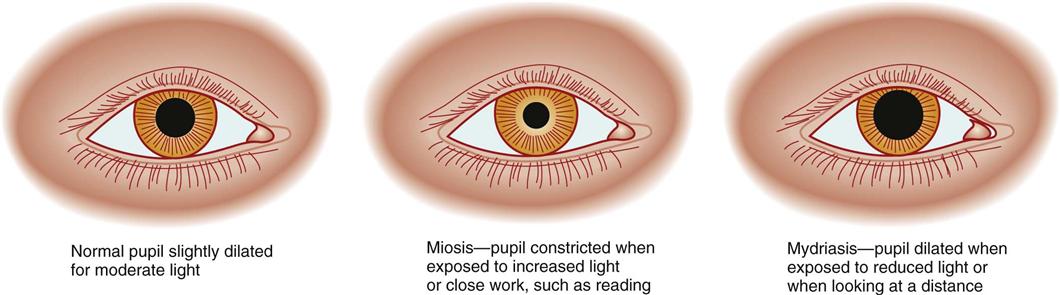
A newborn’s pupils stay small for up to two weeks after birth. AgeĪge-related miosis is common in newborns and in older adults. The leading causes of miosis include age, inflammation, medication, cluster headaches, head injuries, neurosyphilis and a family history of the condition. When a pupil stays shrunken even when not in bright light, a condition of miosis, that indicates an underlying problem.ĭoctors consider pupils abnormal if they do not dilate in the dark and if they do not constrict in brightly lit conditions. The pupil shrinks in bright light to protect the eye from excess light from entering the eye. In most cases, the pupils of both eyes are the same size, regardless of the amount of light. Normal pupil size in adults ranges from 2 to 4 mm in bright light and from 4 to 8 mm in dark conditions. Under normal circumstances, the pupil changes size between 2 to 8 mm throughout the day, depending on lighting conditions. Miosis is an eye condition in which the pupils are routinely too small for the lighting conditions. Small pupils let in less light to the eye, making it more difficult for someone to see clearly.Īge, injuries and inflammation to the eyes, some medications and a family history cause most of the cases of miosis.Īny consistent presenting of miosis is cause to see a doctor because it could be a symptom of another underlying condition that is more serious. Though opioid drugs tend to be among the most common that affect pupil constriction, other medications may also have an effect on the pupils’ ability to dilate.Miosis is a condition in which the pupils of the eyes are always too small, whether in light or dark. Non-Opioid Drugs That Can Cause Constricted Pupils Illegal forms of opioids or opiates include: During use, opioids tend to stimulate the parasympathetic nerve and cause constricted pupils. Generally, drugs classified as opioids will constrict pupils when the drug is ingested. Generally, stimulants dilate pupils and depressants (like opioids) cause constricted pupils. But substance use and abuse can affect the central nervous system and interfere with the ability of the eyes to react appropriately. Usually surrounding light causes stimulation of the relevant nerve to dilate or constrict the pupils. Pupils that do not dilate or constrict properly can create, or be a symptom of, serious vision problems. Pupil dilation and constriction is an important function that controls the amount of light that enters the eye and allows a person to see properly. When the sympathetic nerve is stimulated, pupils dilate. Normally, when the parasympathetic nerve is activated, it causes pupils to constrict, or narrow. Pupil constriction and dilation are controlled by the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems in the brain. One of the more noticeable, and uncontrollable, ways is dilated or constricted pupils.
Physiological changes in the brain can appear in a variety of ways in the rest of the body. On the other hand, depressants generally inhibit brain activity causing drowsiness, lethargy, decreased heart rate, blood pressure, and a sense of calm. For instance, stimulants tend to affect the brain in a way that increases alertness, energy levels, heart rate and blood pressure. How a particular drug affects the body often depends on the type of drug being used. Motivational Interviewing Therapy Program.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
